Backup Plan Maintenance
This guide covers essential maintenance tasks for standard incremental backup plans to keep your backups healthy and storage optimized.
Cleanup / Prune Old Backups
Pruning removes old backup snapshots based on your retention policy, freeing up storage space.
When to Prune
- Automatic: Pruning happens automatically based on your retention settings
- Manual: Run prune when you need to immediately reclaim storage space
- After changing retention: When you reduce the "Snapshots to Keep" setting
How Pruning Works
Your backup plan maintains a specified number of recent snapshots (configured as "Snapshots to Keep"). When you run prune:
- Snapshots exceeding your retention limit are removed
- Only the data blocks are deleted from storage
- Referenced data blocks (used by kept snapshots) remain intact
- Storage space is freed gradually as unreferenced blocks are removed
Running Manual Prune
- Navigate to your backup plan details page
- Click the More Options (⋮) button in the header
- Select "Clean Up"
- Review the prune summary:
- Current snapshot count
- Number of snapshots to be removed
- Retention policy settings
- Click "Yes, Remove Old Backups" to confirm
What You'll See:
- If snapshots exceed your retention limit: Shows how many will be removed
- If within retention limit: "There are no excess snapshots to clean up"
Important Notes:
- Pruning cannot be undone
- The process may take several minutes for large backups
- Active backups are never pruned
- You cannot prune while a backup is in progress
Best Practices
- Let automatic pruning handle routine cleanup
- Manually prune after significantly reducing retention settings
- Run prune during off-hours to avoid performance impact
- Verify storage space after pruning (may take time to reflect)
Unlock Repository
Unlocking removes stale locks from the backup repository that may prevent new backups from running.
When to Unlock
Unlock when:
- A backup appears stuck or won't start
- You see errors about "repository is already locked"
- A backup was forcefully terminated (power loss, crash)
- Previous backup failed with locking errors
What Are Repository Locks?
Restic creates locks to prevent multiple simultaneous backups to the same repository (which could corrupt data). Normally, locks are automatically released when backups complete. However, if a backup crashes or is interrupted, stale locks may remain.
Running Unlock
- Navigate to your backup plan details page
- Click the More Options (⋮) button in the header
- Select "Unlock"
- Read the confirmation message:
- Explains that unlock removes unused locks from failed backups
- Helps start new backups when stuck
- Click "Yes, Unlock" to confirm
What Happens:
- Restic scans the repository for locks
- Identifies and removes stale/inactive locks
- Active locks (from running backups) are preserved
- A success message confirms removal
Important Notes:
- Safe to run - doesn't affect backup data or snapshots
- Only removes locks not associated with active processes
- Run this only when backups are stuck, not routinely
- Cannot unlock while a backup is actively running
Troubleshooting After Unlock
If unlocking doesn't resolve the issue:
- Check storage connectivity (verify in Storages page)
- Ensure source device is accessible
- Review plan logs for other errors
- Verify sufficient storage space available
- Try pausing and resuming the plan
View Plan Logs
Plan logs provide detailed information about all backup operations, useful for troubleshooting and monitoring.
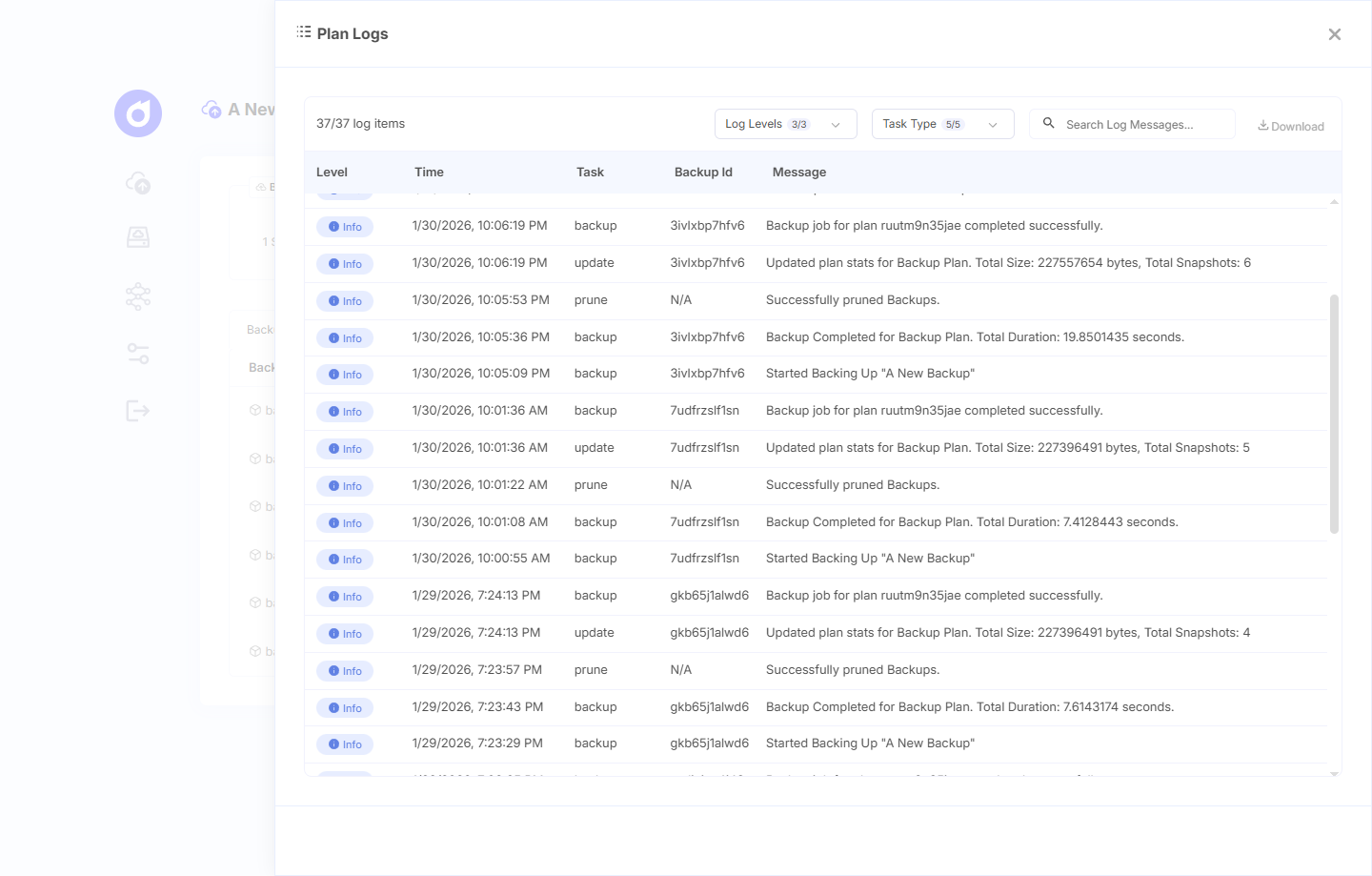
Accessing Logs
- Navigate to your backup plan details page
- Click the More Options (⋮) button in the header
- Select "View Logs"
- A side panel opens with the complete log history
Understanding Log Entries
Logs display chronologically with newest entries at the top. Each entry includes:
Timestamp: Exact date and time of the event
Level: Log severity
- Info - Normal operations (backup started, completed)
- Warn - Non-critical issues (retries, warnings)
- Error - Failures requiring attention
Message: Description of what happened
Common Log Events:
Backup Plan created- Plan initializedBackup started- Backup execution beganBackup completed successfully- Backup finished normallyBackup failed- Backup encountered errorsPlan paused/resumed- Schedule changesBackup Plan updated- Configuration modifiedRepository unlocked- Stale locks removedBackup Plan prune successfully performed- Cleanup completed
Filtering and Searching Logs
- Use the search box to find specific events or errors
- Filter by log level (Info, Warn, Error)
- Click on individual entries to expand full details
- Scroll through history to track patterns
Downloading Logs
To save logs for offline review or support:
- While viewing logs, click "Download Logs" button
- Logs download as a
.logfile - Open with any text editor
- Share with support if needed for troubleshooting
Downloaded Log Format:
- JSON format for structured analysis
- Each line is a complete log entry
- Includes all metadata (timestamps, levels, context)
Reading Backup Progress in Logs
During active backups, logs show:
- Files being scanned and processed
- Data blocks being uploaded
- Progress percentages
- Any files skipped or excluded
- Errors encountered during operation
Using Logs for Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Log Indicators:
"Permission denied" errors:
- Check source paths have proper access rights
- Verify service account permissions
"Connection refused/timeout":
- Storage connectivity issues
- Check network and storage configuration
"Repository locked" errors:
- Another backup may be running
- Stale lock needs removal (use Unlock)
"Out of space" errors:
- Storage quota exceeded
- Run prune or add storage capacity
"No such file or directory":
- Source paths moved or deleted
- Update plan source configuration
Log Retention
- Logs are stored in
data/logs/directory - Log file named
plan-{planId}.log - Logs persist until plan is deleted
- Large log files may be rotated automatically
- No automatic cleanup - manage manually if needed
Storage Optimization
- Review retention policies - Balance history vs. storage costs
- Use compression - Enable if not already active
- Prune regularly - Remove unneeded snapshots
- Monitor growth - Track backup size trends over time
- Clean test plans - Remove experimental or test backup plans
Maintenance Checklist
Use this checklist for routine backup plan health checks:
- Recent backups completed successfully (check history)
- No persistent errors in logs (review warnings/errors)
- Storage usage is within acceptable limits
- Snapshot count aligns with retention policy
- Backup times are consistent and reasonable
- No stuck or locked repositories
- Source paths are still accessible
- Schedule is appropriate for current needs
Recommended Frequency:
- Weekly: Quick status check, review recent backup history
- Monthly: Full log review, verify retention, test restore
- Quarterly: Review and optimize retention policies, prune if needed
Quick Reference
| Task | When | How | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prune | Storage optimization needed | More Options → Clean Up | Removes old snapshots, frees space |
| Unlock | Backup stuck/won't start | More Options → Unlock | Removes stale locks |
| View Logs | Troubleshooting issues | More Options → View Logs | Shows detailed operation history |
| Download Logs | Need offline analysis | In logs panel → Download | Saves logs as file |
Regular maintenance keeps your backup plans running smoothly and ensures your data remains protected and accessible.